Spectral analysis options
Click on the button Options to see/change the parameters.
-
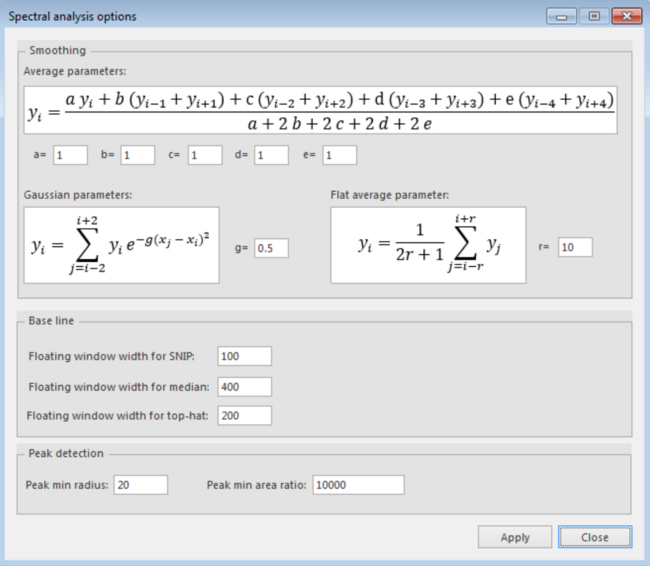
Average parameters (custom average smoothing):
The equation that is used is displayed on the top and the ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’ and ‘e’ are parameters that can be set as preferred to calculate the average.
a = Multiplication of the original value. Typical value: 4.0. Valid range: -10 to 10.
b = Multiplication of the values just before and after the original value. Typical value: 2.0. Valid range: -10 to 10.
c = Multiplication of the values 2 places before and after the original value. Typical value: 1.0. Valid range: -10 to 10.
d = Multiplication of the values 3 places before and after the original value. Typical value: 0.5. Valid range: -10 to 10
e = Multiplication of the values 4 places before and after the original value. Typical value: 0.25. Valid range: -10 to 10
-
Gaussian parameter (gauss smoothing):
The smaller the value the stronger the smoothing. If g =0.0, this is an average smoothing on 5 values. If g >= 5.0, the smoothing is nearly undetectable. Valid range: 0.0 to 5.0.
-
Flat average parameter (wide average smoothing):
‘r’ is number of points taken into account on either side. This means for the value 10 that there will be 10 point on the left and 10 on the right used.
-
Floating window width for SNIP. This is the width of the floating window used to compute the base line, in value index, not in X value. So if value is 20, the 10 points before and after the middle point are used during computation.
-
Floating window width for median. This is the width of the floating window used to compute the base line, in value index, not in X value. So if value is 20, the 10 points before and after the middle point are used during computation. Typical values are from 20 to 800. Start trial around 2% of the number of points in the spectra. Valid range is from 4 to 10.000.
-
Floating window width for top-hat. This is the width of the floating window used to compute the base line, in value index, not in X value. So if value is 20, the 10 points before and after the middle point are used during computation. Typical values are from 20 to 200. Valid range is from 4 to 10.000.
-
Peak detection radius. This value represents the number of points used to find the valley points. If this value is 20, this means that a point is a valley point if the 20 points left and right are greater. Curve fittings used during peak detection are considering twice this number of points. Typical value is 40.
-
Peak minimum area ratio. If this value is 1000, peaks having a surface lower than the whole spectrum surface divided by 1000 (or 1%) are discarded. Typical value is 10.000.

